
By following these steps, companies can accurately estimate the salvage value of their assets and make informed decisions about their financial management. Market conditions play a significant role in determining an asset’s salvage value. The balance between supply and demand in the resale market affects an asset’s salvage value, with high demand leading to higher salvage values and low demand resulting in lower values.

Double-Declining Balance
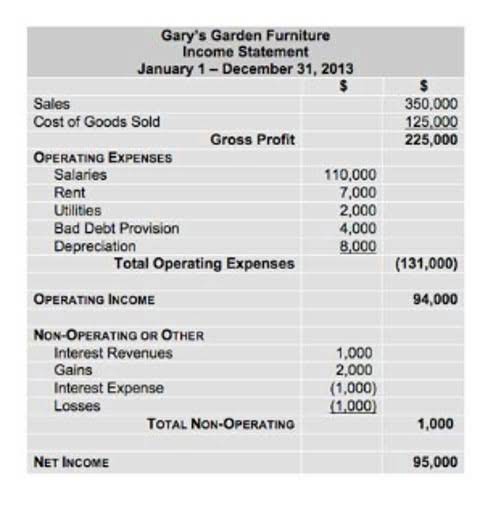
The carrying value is what the item is worth on the books as it’s losing value. When calculating depreciation, you subtract the salvage value from the initial cost. To illustrate this, consider the example of a car that has been totaled and sold for scrap metal. salvage value formula The difference between the initial purchase price and the amount it sold for is the salvage value. This accelerated depreciation method assumes assets lose more value in their early years.
Unlock Your Business Potential with OneMoneyWay

The IRS Collection Statute Expiration Date (CSED) is a 10-year period during which the IRS can collect outstanding tax debts. Factors such as bankruptcy, installment agreements, and offers in compromise can extend this period. Understanding the CSED helps taxpayers manage obligations and avoid prolonged collection https://siddhtours.com/how-to-calculate-shareholders-equity-9-steps-with/ actions. Salvage value and depreciation are both accounting concepts that are related to the value of an asset over its useful life.
- External factors like technological advancements, supply and demand, and economic conditions also impact salvage value, making market analysis an essential part of the calculation.
- This differs from book value, which is the value written on a company’s papers, considering how much it’s been used up.
- It includes equal depreciation expenses each year throughout the entire useful life until the entire asset is depreciated to its salvage value.
- C) Multiply the depreciation per unit by the actual number of units produced in that period.
- Tracking usage patterns is crucial in estimating residual value accurately, as it helps account for the asset’s condition at the end of its useful life.
How to Calculate Salvage Value for Business and Personal Assets
- In conclusion, knowing how to calculate an asset’s salvage value is a vital aspect of financial planning and accounting.
- Inflation affects the real value of money and can impact the salvage value of assets.
- Several of the depreciation functions include optional arguments to allow for more complex facts, such as partial-year depreciation.
- The declining balance method is an accelerated approach, recording higher depreciation expenses early in an asset’s life and lower expenses later.
Businesses that invest in maintenance can sometimes increase the salvage value of their assets. This means that after 15 years, the asset is assumed to be worth $10,000, either for resale or scrap metal. If the machinery is well-maintained and technology hasn’t advanced too much, it might even sell for more than its salvage value.
- X wants to charge depreciation using the diminishing balance method and wants to know the amount of depreciation it should charge in its profit and loss account.
- It’s based on what the company thinks they can get if they sell that thing when it’s no longer useful.
- The straight-line method is a way to calculate depreciation by evenly spreading the asset’s cost over its useful life.
- Salvage value can be considered the price a company could get for something when it’s all used up.
Understanding this value is essential for accurate depreciation accounting and for making informed decisions about when to retire or replace an asset. Salvage value is subtracted from an asset’s purchase cost to determine the total amount that can be depreciated over its useful life. This calculation ensures that depreciation expenses reflect the asset’s anticipated residual value, leading to more accurate financial reporting. In the straight-line method, salvage value is deducted from the purchase price before dividing by useful life, ensuring depreciation is spread evenly. In declining balance depreciation, businesses often ignore retained earnings balance sheet salvage value until the end of an asset’s life.

